A tsunami advisory was in effect for the Southern California coast Saturday morning after a volcano erupted near the Pacific nation of Tonga.
Beaches and piers were closed from San Diego to the Bay Area as a precaution because of higher-than-normal waves. While there were “no significant concerns about inundation,” the National Weather Service tweeted that strong rip currents were possible. Officials urged people to stay out of the water.
The weather service said the tsunami activity was supposed to hit the Southern California coastline beginning around 7:45 a.m. However, there were no significant concerns about inundation and the main concerns were over strong rip current, the agency said.
The weather service warned that even smaller tsunamis can be dangerous, as “strong currents can damage boats and infrastructure in harbors.”
“How the tsunami affects an area has a lot to do with timing,” NWS said in a tweet. “There’s been some issues up north this [morning], with the surge coming in at high tide. As we head to low tide, harbors will want to be on the lookout for water getting too low.”
The Orange County Sheriff’s Department said in an advisory that all beaches, piers and marinas were closed until further notice, as strong currents were expected in harbors and bays for several hours.
“Although no significant coastal flooding is expected, some areas could experience dangerous currents and tidal surges due to this tsunami along beaches and in harbors and marinas,” the Orange County Sheriff’s Department said in a news release. “The impact of this tsunami will be stronger than normal currents and possible higher than normal tidal surges along the beaches.”
By 7:46 p.m., that advisory was canceled, the NWS said on Twitter.
“Some minor fluctuations above/below normal tide levels are possible over the next few hours,” the agency added.
Los Angeles County officials said residents living within a tsunami advisory area should do the following:
- Move out of the water, off the beach and away from harbors, marinas, breakwaters, bays and inlets.
- Do not go to the shore to observe the tsunami.
- Do not return to the coast until local emergency officials indicate it is safe.
In Berkeley, officials closed the city’s marina and urged people to seek higher ground. The Berkeley Fire Department issued a mandatory evacuation for the marina area as 2- to 3-foot waves were expected to arrive at about 7:30 a.m.
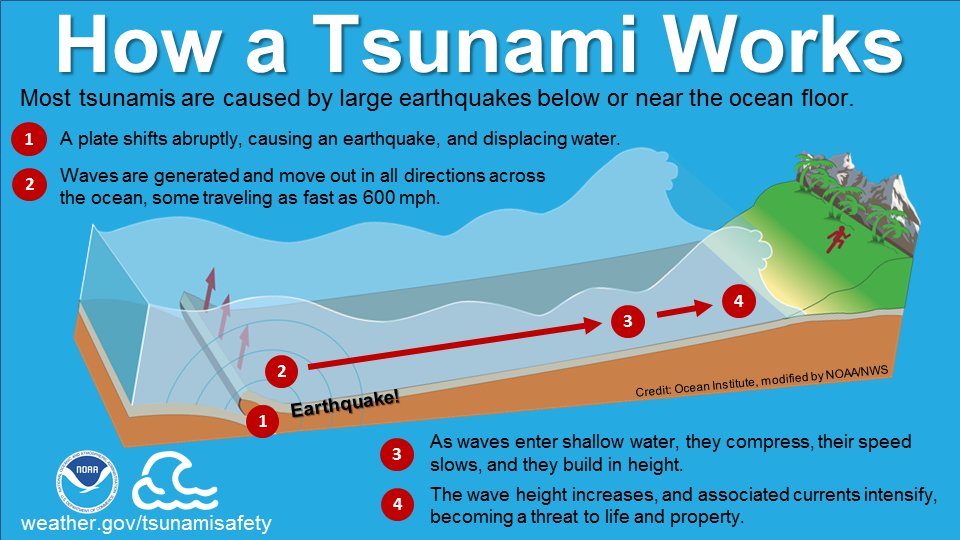
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, a tsunami is a series of extremely long waves caused by a large and sudden displacement of the ocean. Most tsunamis are usually the result of an earthquake below or near the ocean floor, which makes Saturday’s advisory uncommon.
“Most often it’s from plates shifting abruptly on the sea floor,” the weather service tweeted. This tsunami was essentially caused by a massive underwater explosion of molten rock and lava that displaced the water above it.
The tsunami threat around the Pacific from a huge undersea volcanic eruption began to recede Sunday, while the extent of damage to Tonga remained unclear.
Satellite images showed the spectacular eruption that took place Saturday evening, with a plume of ash, steam and gas rising like a mushroom above the blue Pacific waters. A sonic boom could be heard as far away as Alaska.
In Tonga it sent tsunami waves crashing across the shore and people rushing to higher ground.
The eruption cut the internet to Tonga, leaving friends and family members around the world anxiously trying to get in touch to figure out if there were any injuries and the extent of the damage. Even government websites and other official sources remained without updates on Sunday afternoon.
New Zealand Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern said there had not yet been any official reports of injuries or deaths in Tonga, but cautioned that authorities hadn’t yet made contact with some coastal areas and smaller islands.
“Communication with Tonga remains very limited. And I know that is causing a huge amount of anxiety for the Tongan community here,” Ardern said.
She said there had been significant damage to boats and shops along the Tongan coastline. The capital, Nuku’alofa, was covered in a thick film of volcanic dust, Ardern said, contaminating water supplies and making fresh water a vital need.
Aid agencies said thick ash and smoke had prompted authorities to ask people to wear masks and drink bottled water.
Ardern said New Zealand was unable to send a military surveillance flight over Tonga on Sunday because the ash cloud was 63,000 feet (19,000 meters) high but they hoped to send the flight on Monday, followed by supply planes and navy ships.
One complicating factor to any international aid effort is that Tonga has so far managed to avoid any outbreaks of COVID-19. Ardern said New Zealand’s military staff were all fully vaccinated and willing to follow any protocols established by Tonga.
Dave Snider, the tsunami warning coordinator for the National Tsunami Warning Center in Palmer, Alaska, said it was very unusual for a volcanic eruption to affect an entire ocean basin, and the spectacle was both “humbling and scary.”
The tsunami waves caused damage to boats as far away as New Zealand and Santa Cruz, California, but did not appear to cause any widespread damage. Snider said he anticipated the tsunami situation in the U.S. and elsewhere to continue improving.
Tsunami advisories were earlier issued for Japan, Hawaii, Alaska and the U.S. Pacific coast. The U.S. Geological Survey estimated the eruption caused the equivalent of a magnitude 5.8 earthquake. Scientists said tsunamis generated by volcanoes rather than earthquakes are relatively rare.
The Tonga Meteorological Services said a tsunami warning was declared for all of the archipelago, and data from the Pacific tsunami center said waves of 80 centimeters (2.7 feet) were detected.
Rachel Afeaki-Taumoepeau, who chairs the New Zealand Tonga Business Council, said she hoped the relatively low level of the tsunami waves would have allowed most people to get to safety, although she worried about those living on islands closest to the volcano. She said she hadn’t yet been able to contact her friends and family in Tonga.
“We are praying that the damage is just to infrastructure and people were able to get to higher land,” she said.
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken wrote on Twitter he is “deeply concerned for the people of Tonga as they recover from the aftermath of a volcanic eruption and tsunami. The United States stands prepared to provide support to our Pacific neighbors.”
Tonga gets its internet via an undersea cable from Suva, Fiji. All internet connectivity with Tonga was lost at about 6:40 p.m. local time, said Doug Madory, director of internet analysis for the network intelligence firm Kentik.
On Tonga, which is home to about 105,000 people, video posted to social media showed large waves washing ashore in coastal areas and swirling around homes, a church and other buildings. A Twitter user identified as Dr. Faka’iloatonga Taumoefolau posted video showing waves crashing ashore.
“Can literally hear the volcano eruption, sounds pretty violent,” he wrote, adding in a later post: “Raining ash and tiny pebbles, darkness blanketing the sky.”
The explosion of the Hunga Tonga Hunga Ha’apai volcano was the latest in a series of dramatic eruptions.
Earth imaging company Planet Labs PBC had watched the island in recent days after a new volcanic vent there began erupting in late December.
Satellite images captured by the company show how drastically the volcano had shaped the area, creating a growing island off Tonga.
“The surface area of the island appears to have expanded by nearly 45% due to ashfall,” Planet Labs said days before the latest activity.
Following Saturday’s eruption, residents in Hawaii, Alaska and along the U.S. Pacific coast were advised to move away from the coastline to higher ground and to pay attention to instructions from their local emergency management officials, said Snider.
“We don’t issue an advisory for this length of coastline as we’ve done — I’m not sure when the last time was — but it really isn’t an everyday experience,” Snider said.
Savannah Peterson watched in shock as the water rose several feet in a matter of minutes in front of her oceanfront house in Pacifica, California, just south of San Francisco.
“It came up so fast, and a few minutes after that it was down again. It was nuts to see that happen so quickly,” she said. “I’ve never had water come all the way up to my front door, and today it did.”
Police rescued a surfer whose surfboard broke in powerful waves off San Francisco.
Farther south in Santa Cruz, California, officials were taking stock of damage after a surge damaged boats and inundated low-lying streets and parking lots, sending cars afloat.
In Southern California, surging waters sunk at least one boat in Ventura Harbor northwest of Los Angeles.
New Zealand’s private forecaster, Weather Watch, tweeted that people as far away as Southland, the country’s southernmost region, reported hearing sonic booms from the eruption. Others reported that many boats were damaged by a tsunami that hit a marina in Whangarei, in the Northland region.
Earlier, the Matangi Tonga news site reported that scientists observed massive explosions, thunder and lightning near the volcano after it started erupting early Friday. Satellite images showed a 5-kilometer (3-mile) -wide plume rising into the air to about 20 kilometers (12 miles).
The Hunga Tonga Hunga Ha’apai volcano is located about 64 kilometers (40 miles) north of Nuku’alofa. In late 2014 and early 2015, a series of eruptions in the area created a small new island and disrupted international air travel to the Pacific archipelago for several days.
There is not a significant difference between volcanoes underwater and on land, and underwater volcanoes become bigger as they erupt, at some point usually breaching the surface, said Hans Schwaiger, a research geophysicist with the Alaska Volcano Observatory.
With underwater volcanoes, however, the water can add to the explosivity of the eruption as it hits the lava, Schwaiger added.
Before an explosion, there is generally an increase in small local earthquakes at the volcano, but depending on how far it is from land, that may not be felt by residents along the shoreline, Schwaiger said.
In 2019, Tonga lost internet access for nearly two weeks when a fiber-optic cable was severed. The director of the local cable company said at the time that a large ship may have cut the cable by dragging an anchor. Until limited satellite access was restored people couldn’t even make international calls.
Southern Cross Cable Network’s Veverka said limited satellite connections exist between Tonga and other parts of the world but he did not know if they might be affected by power outages.