What worries him most are the three power plants looming over the Oxnard coast, and the toxic waste site that has languished there for decades. There are also two naval bases, unknown military dumps and a smog-spewing port. Just one flood could unleash a flow of industrial chemicals and overwhelm his working-class, mostly Latino community.
“The coast of California is marked by massive inequality. People don’t realize that because they go to Malibu, they go to Santa Barbara. Those are the beaches that people see and are familiar with,” said Zucker, a longtime advocate for environmental justice. “They don’t think of places like Wilmington, West Long Beach, Barrio Logan, West Oakland, Richmond, Bayview-Hunters Point. You can name all these communities, and it’s the same story.”
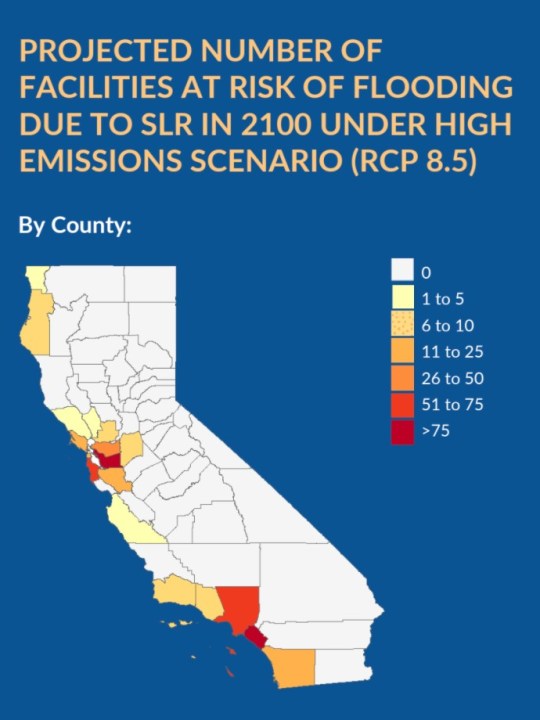
These predominately Black and brown communities, in fact, are five times more likely than the general population to live within half a mile of a toxic site that could flood by 2050, according to a new statewide mapping project led by environmental health professors at UC Berkeley and UCLA. All told, the ocean could inundate more than 400 hazardous facilities by the end of the century — exposing nearby residents to dangerous chemicals and polluted water.
This three-year project, dubbed Toxic Tides, is the first systematic look at the environmental justice ramifications of sea level rise and hazardous sites along the entire coast of California. In collaboration with advocates like Zucker, researchers created a series of searchable maps that piece together where in California this flooding could occur, which industrial facilities face particularly risk, and how these threats disproportionately affect lower-income communities of color.
Read the full story on LATimes.com.